How does it work?
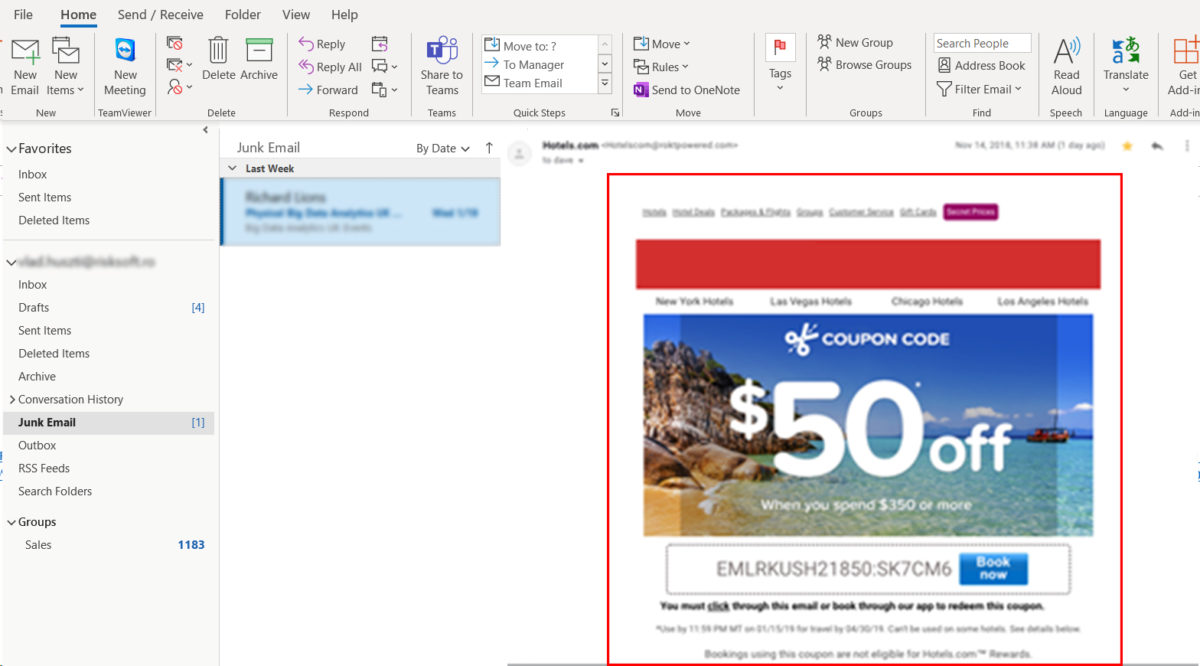
Usually, phishing attacks manifest by sending to the targeted person (regular employees or management team), spoof emails carrying hacked links. Here, cybercriminals steal the private information entered by the user in the spoofed website. Users must stay alert to prevent attacks and avoid being the victims of different thefts such as unauthorized purchases or stealing funds.
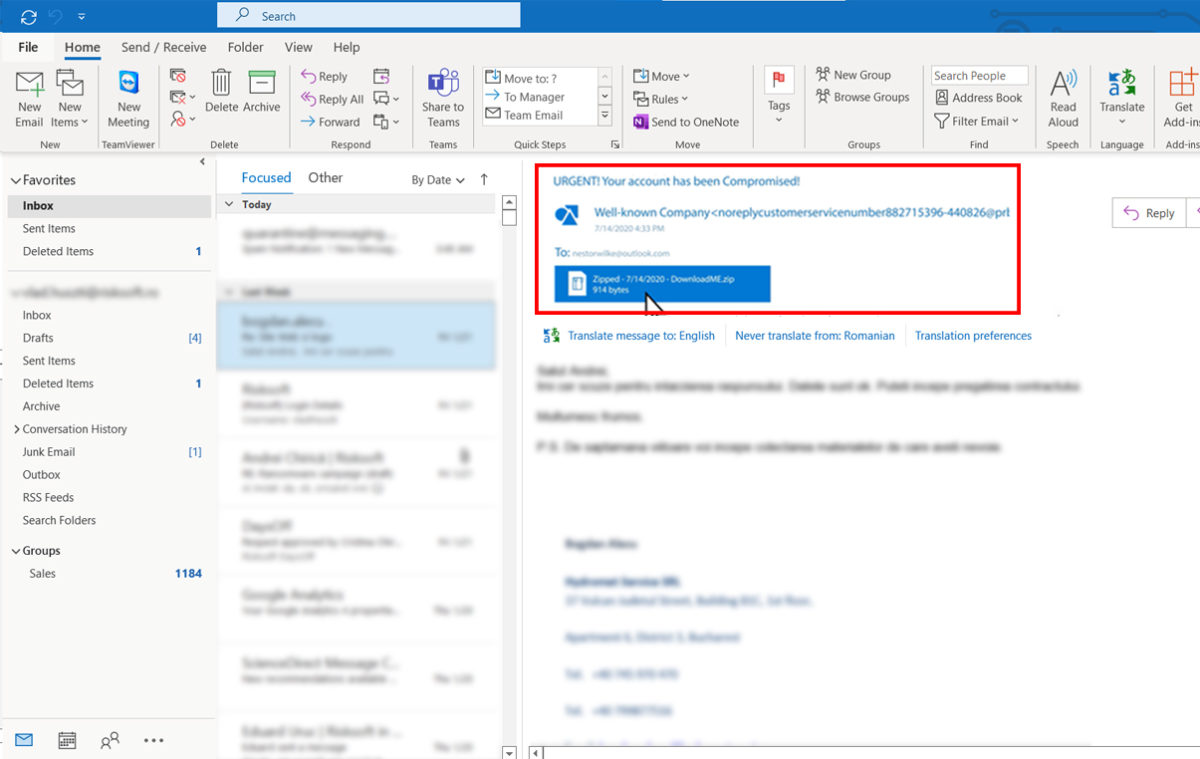
Phishing is characterized as a delivery mechanism for different malware that usually targets organizations. Usually, the malware arrives as a link or attachment in an email, pretending to be from a well-known person or company to trick you.
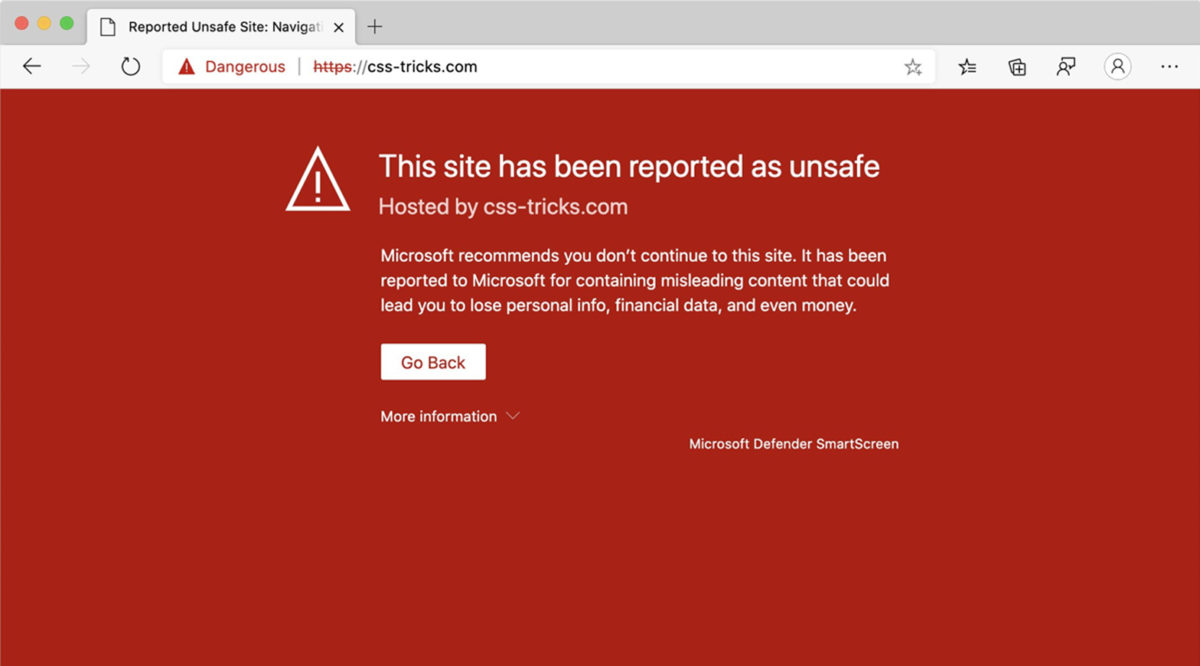
Some of the most common phishing attacks come from spam emails, which you need to be aware of. Such faked emails include links (URLs) to websites under attackers’ control that are modified to look like legitimate mail, implementing a fake URL that directs the user to visit the fake (spoof) website where the attacker can steal the most sensitive information.
Therefore, once the host has entered the spoofed link, phishing aims to inject malware into the user’s private system, helping the attacker to steal the private information from the system without the knowledge of the user. Such injected malware are viruses known as Ransomware, Trojan horse; Worm; Spyware.
The system which is infected with malware is termed as zombie and such zombie is used to launch criminal activities.
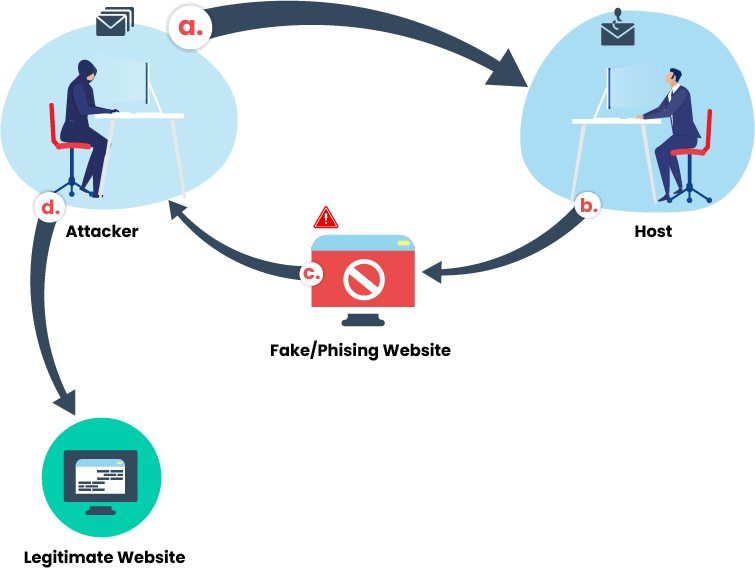
a. Attacker sends an email with a spoofed website to the legitimate host
b. Host without knowing it is a phishing attempt, just click the URL in the mail and visit the fake website
c. Once the host enters the credentials (in the spoofed website), the attacker now can steal that sensitive information
d. The attacker uses the credentials of the host on the original website and steals the employee’ identity
Real-life situations
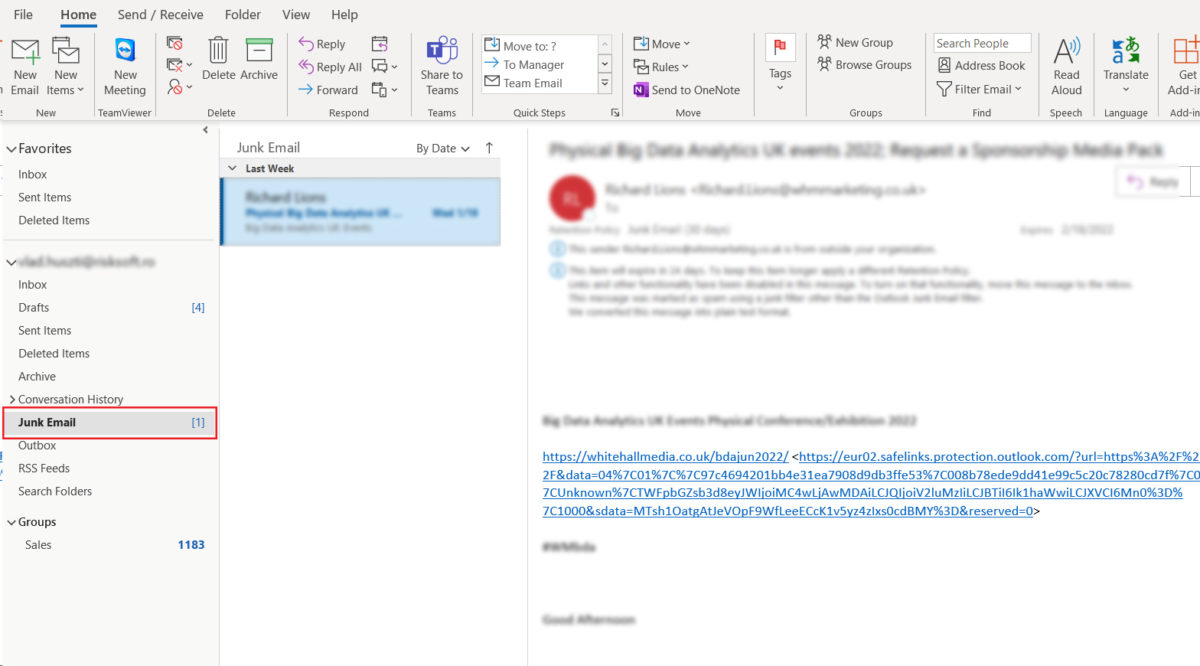
Two examples of Email Phishing attacks that happen in corporations
Corporate emails
An employee receives an e-mail from the executive director of his company, asking him to buy electronic gift cards for a customer appreciation event. The request is urgent, so she buys these gift cards online and sends the numbers to the CEO. A few weeks later, the employee discovered that the executive director had not made this request.
Cloud email or fake web-links
An employee receives an email with a link to a secure document. He enters his credentials to view the document, but the document does not load. Then the employee moves on to another task and forgets about the error. The employee provided the username and password to the hackers, who can now use it to access his/her email and other online accounts, including the systems and data used by the company.
If you suspect any phishing attack do not hesitate to contact our qualified technicians.
For more information please contact us at solutions@risksoft.ro
How to protect your business?
Let’s recap. What you should be aware of?
A good practice is to always delete the messages and emails that are unwelcome and with whom the victim has no real connection. For those who fall into this category, it is recommended to ask the opinion of a qualified person about how to proceed next.
1
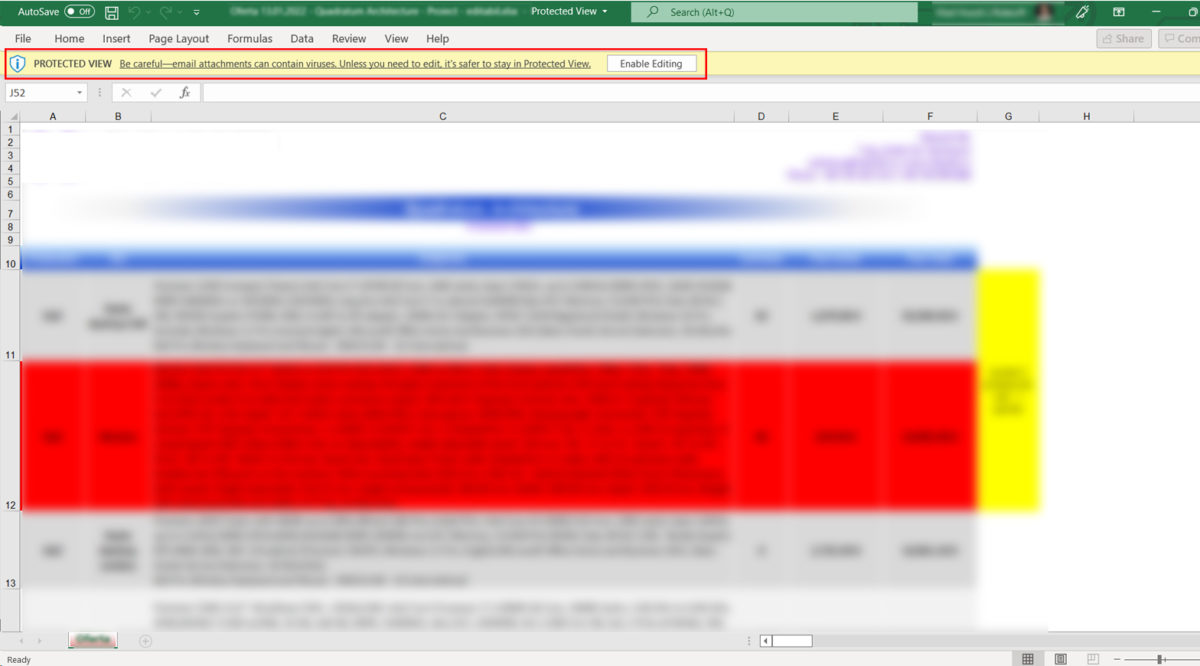
Avoid hacked attachments
Never open attachments you don’t seem right and be careful when accessing emails, even if they appear to come from well-known sources, such as colleagues or business partners.
Phishing emails are often having information that asks the users to enter sensitive information or urge them to click attachments. Before entering any attachment, first, check the sender’s email address (not the displayed name).
4
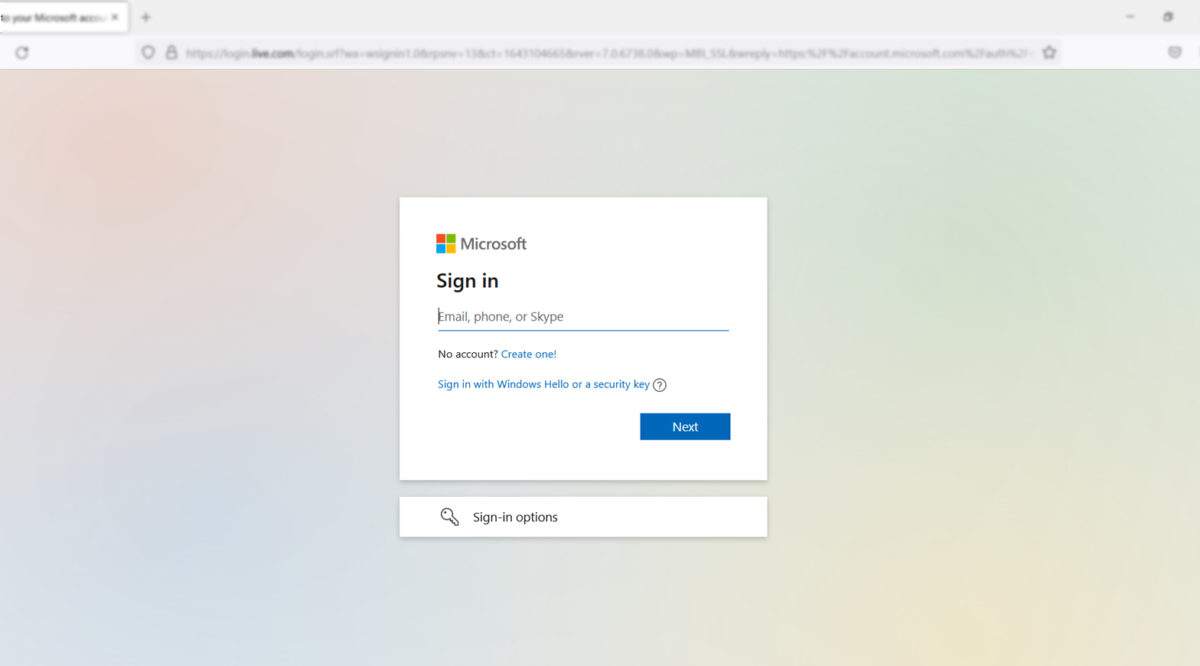
Avoid writing your credential
Avoid clicking on the action buttons such as “Verify YOUR ACCOUNT”. Such links may lead to a webpage that looks identical to the real webpage, but which is controlled by the attacker. On this page, the user is prompted to log in. Finally, any captured usernames and login credentials are sent to the phisher.